Do I know how each medication helps me?
Your doctor may prescribe medications to:
- prevent blood clots
- regulate your heart rhythm
- lower your blood pressure
- lower the bad cholesterol levels in your blood
- manage your blood sugar levels
It is a good idea to get all your prescriptions filled at the same pharmacy.

It is important that you have the information you need to use your medications safely. Download the set of 5 questions to ask about your medications to help you start a conversation with your health care team.
Medications help lower your risk of having another stroke. Take each medication as directed by the doctor. Even if you feel well, continue to take your medication. Do not stop taking any medications without talking to your health care provider first.
Do I know if these medications interact with other medications I take and the food I eat?
Check with your pharmacist or doctor before taking any new medications. This includes:
- prescription medications
- over-the-counter medications such as aspirin, laxatives, cough and cold medicines, pain medications, vitamins and herbal remedies
Do I need a way to organize my medications?
The pharmacist can suggest ways to make it easier to take your medications, such as:
- using a pill box (dosette)
- packaging the medication in single doses (blister pack)

Do I know how to identify the medicines I take?
Below is a list of common types of medications used to prevent stroke. Please note that this is not a complete list of all medications used for this purpose.
- Each type of medication shows a picture of the pills.
- The pills are listed with the generic name first, followed by the brand name (in brackets).
- There may be more than one brand of the same medication so pictures may vary.
- Each picture shows the front and back of one pill or capsule.
- Platelet Inhibitors (stop platelets from sticking together)
- Anticoagulants (prevent blood clots)
- Ace Inhibitors (Lower blood pressure)
- Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers (Lower blood pressure)
- Beta Blockers (Lower blood pressure and heart rate)
- Calcium Channel Blockers (Lower blood pressure and heart rate)
- Diuretics (Lower blood pressure)
- Lipid Lowering Agents (Lower bad cholesterol)
Medication instructions
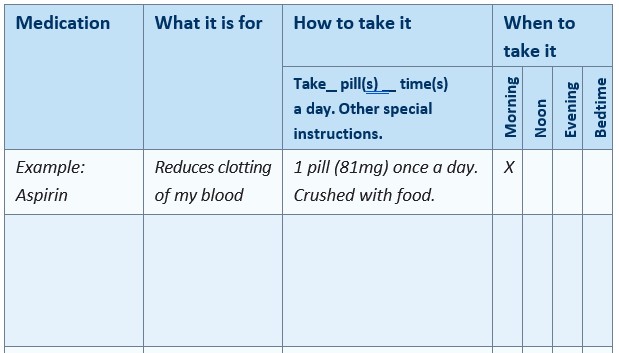
A chart, like the one seen below, can help you keep track of what medications have been prescribed to you, what they’re used for, how to take them, and when to take them. If you need help filling this form out, talk to your pharmacist or doctor.
Keep your chart up to date. Review it regularly with your doctor and pharmacist. You can also create a personalized medication record online that can be saved to your computer.
Medication tracker
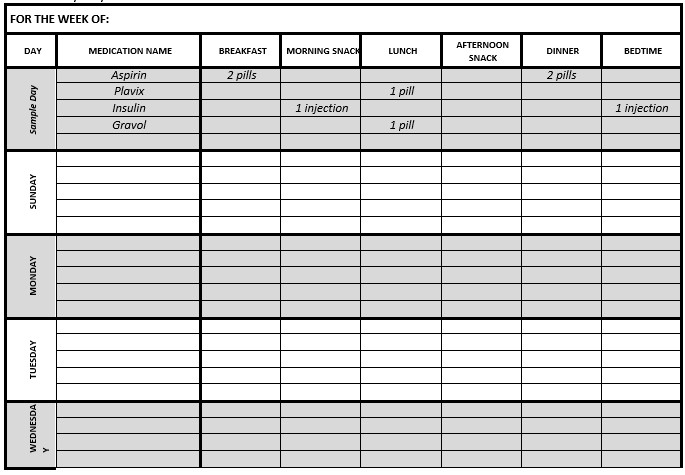
A chart , like the one seen below, can help you make sure that you’ve taken all of your medications. Make sure to check off each dose after you’ve taken it.
- Write in your medications in the “MEDICATION NAME” column
- For each medication, fill in the dose under when you have to take it
- When you’ve taken the dose, cross out the box
- Repeat for every day of the week
Having read the information in this section, consider the following:
- Do I have a list of medications I need to take?
- Do I know how to take each medication (for example: with meals, by mouth, injection, or crushed)?
- Do I know when to take each medication?
- Do I need reminders about when to take each medication?
- Does the pharmacy I use deliver medications to the home?
