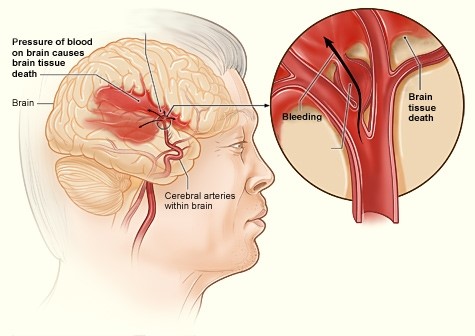
A hemorrhagic stroke occurs when an unhealthy blood vessel that supplies the brain bursts and bleeds. Brain cells and tissues begin to die from lack of oxygen and nutrients. In addition, blood leaks inside the brain causing a sudden increase in pressure which can lead to further brain damage. There are two types of hemorrhagic strokes:
Intracerebral hemorrhage
When an unhealthy blood vessel deep inside the brain bursts. This type of stroke often happens in the basal ganglia, cerebellum, brainstem or cortex.
Subarachnoid hemorrhage
When a blood vessel in the subarachnoid space (the space between the brain and the thin tissues covering the brain) bursts. This causes pressure and cuts off blood supply to the nearby parts of the brain. This type of stroke is often caused by an aneurysm (a bulge or ballooning in a blood vessel caused by weakening of the artery wall) that leaks or bursts.